Resveratrol mitigates lipopolysaccharide-mediated acute inflammation in rats by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κBp65/MAPKs signaling cascade. - Abstract - Europe PMC
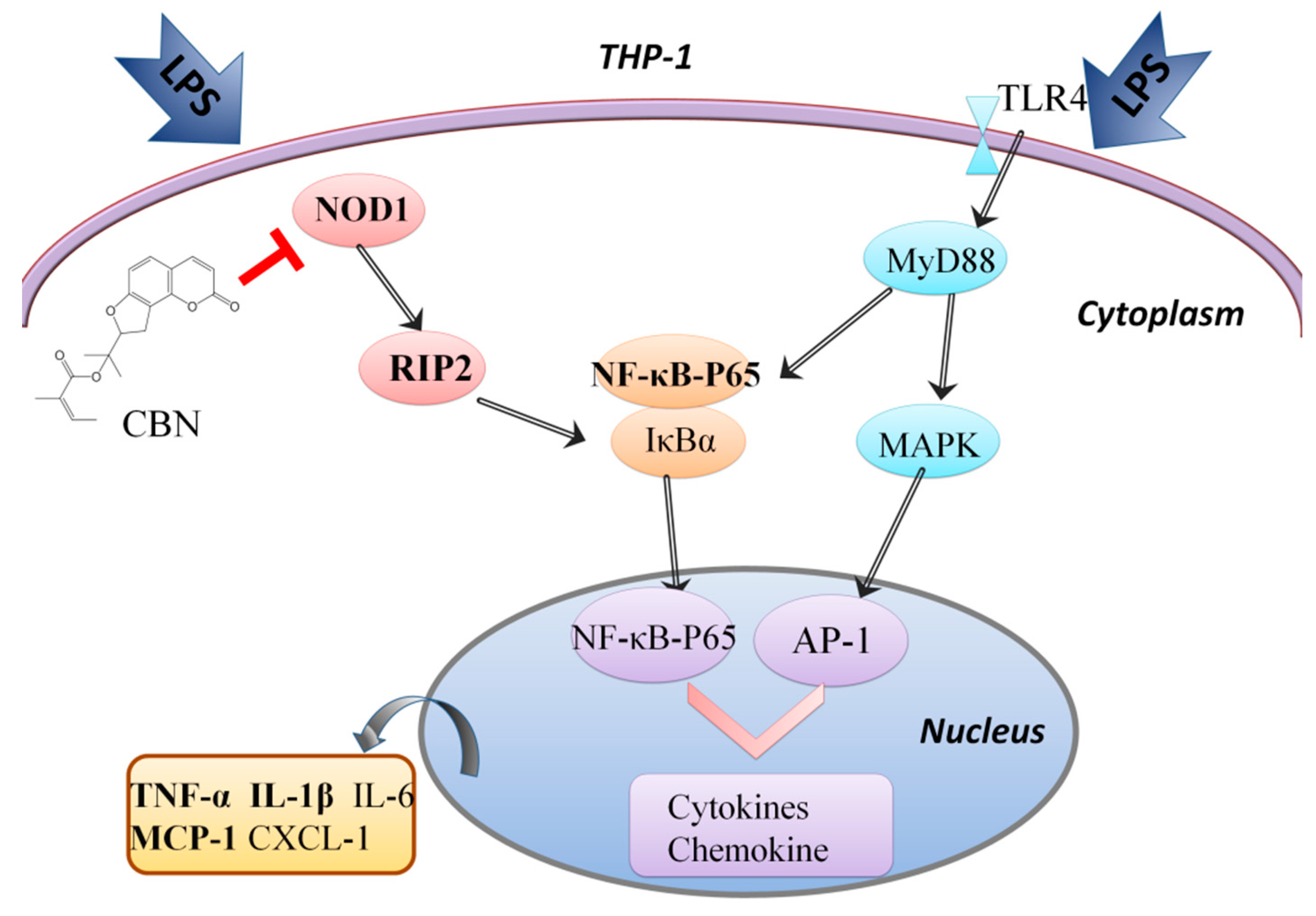
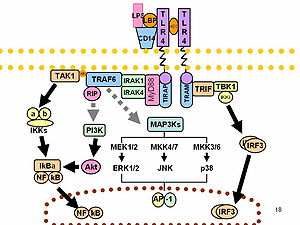
Molecules | Free Full-Text | Columbianadin Suppresses Lipopolysaccharide ( LPS)-Induced Inflammation and Apoptosis through the NOD1 Pathway | HTML
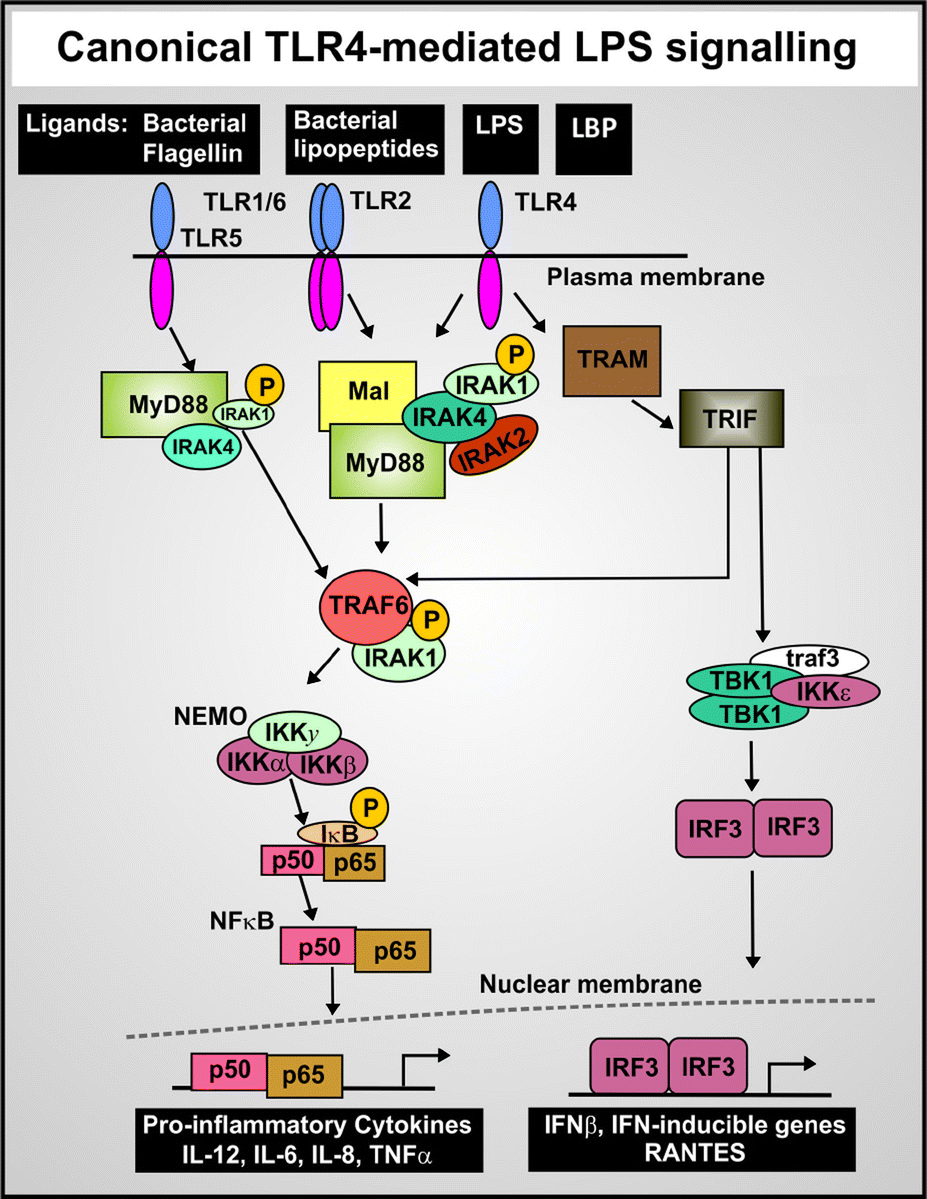
On the translocation of bacteria and their lipopolysaccharides between blood and peripheral locations in chronic, inflammatory diseases: the central r ... - Integrative Biology (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/C5IB00158G

3, 4‐dihydroxybenzalacetone attenuates lipopolysaccharide‐induced inflammation in acute lung injury via down‐regulation of MMP‐2 and MMP‐9 activities through suppressing ROS‐mediated MAPK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways | Semantic Scholar

Directly interact with Keap1 and LPS is involved in the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of (-)-epicatechin-3-gallate in LPS-induced macrophages and endotoxemia - ScienceDirect
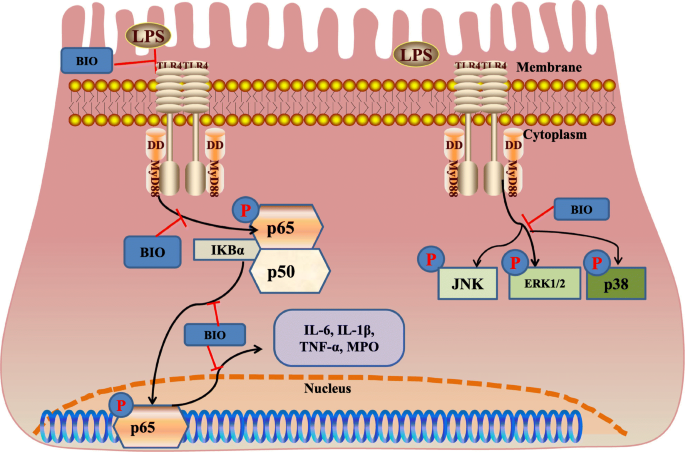
6-Bromoindirubin-3′-Oxime Suppresses LPS-Induced Inflammation via Inhibition of the TLR4/NF-κB and TLR4/MAPK Signaling Pathways | SpringerLink

Lipopolysaccharide Induces GFAT2 Expression to Promote O-Linked β-N-Acetylglucosaminylation and Attenuate Inflammation in Macrophages | The Journal of Immunology
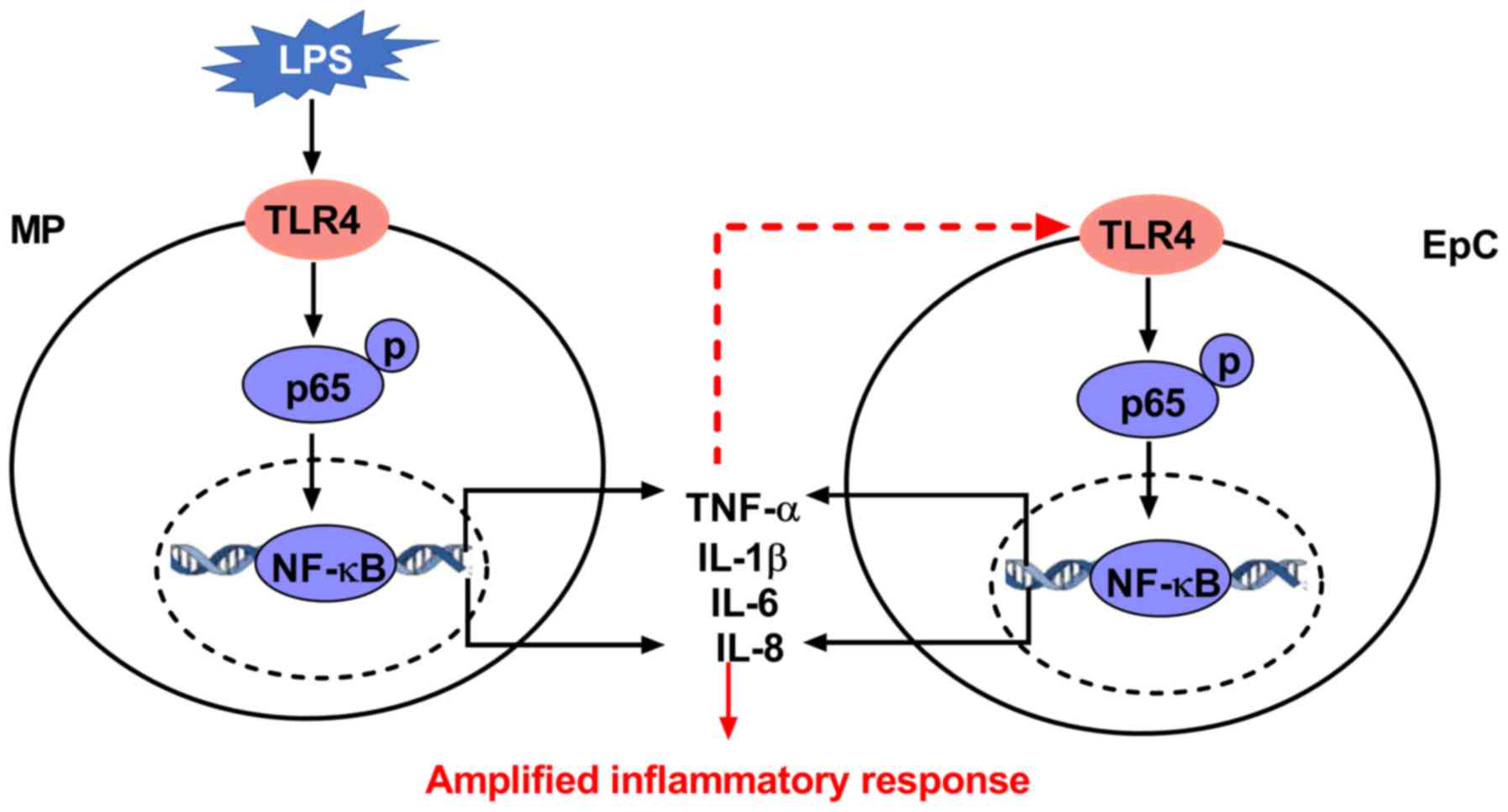
Mechanisms of the lipopolysaccharide‑induced inflammatory response in alveolar epithelial cell/macrophage co‑culture

Inhibitory effects of geraniin on LPS-induced inflammation via regulating NF-κB and Nrf2 pathways in RAW 264.7 cells - ScienceDirect
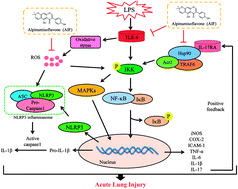
Alpinumisoflavone attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by regulating the effects of anti-oxidation and anti-inflammation both in vitro and in vivo - RSC Advances (RSC Publishing)
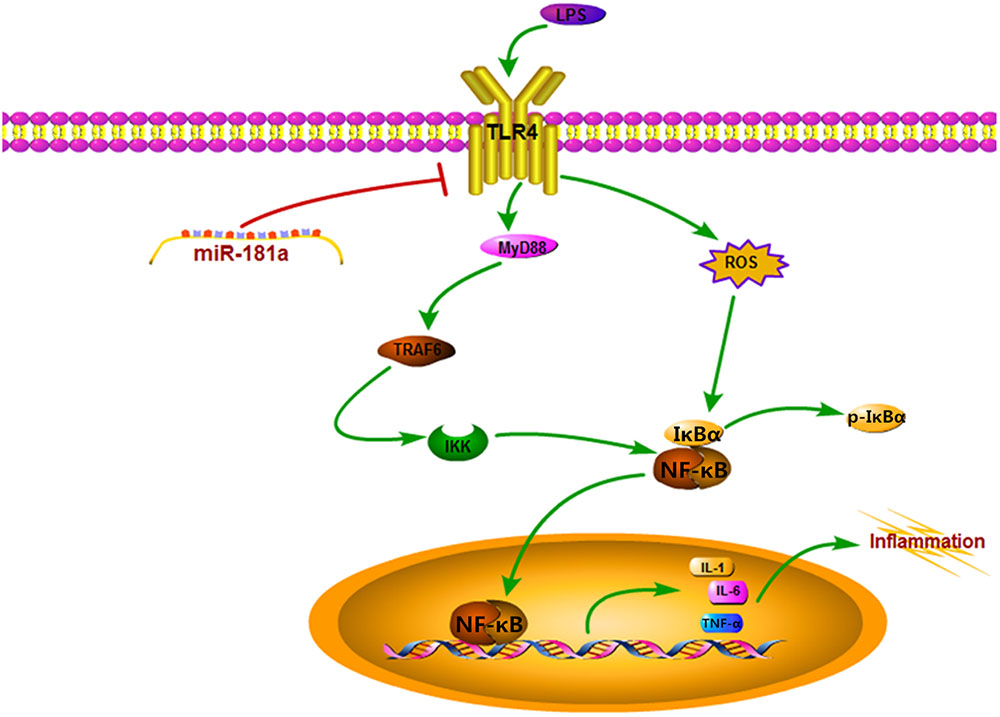
Frontiers | Downregulation of TLR4 by miR-181a Provides Negative Feedback Regulation to Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation | Pharmacology
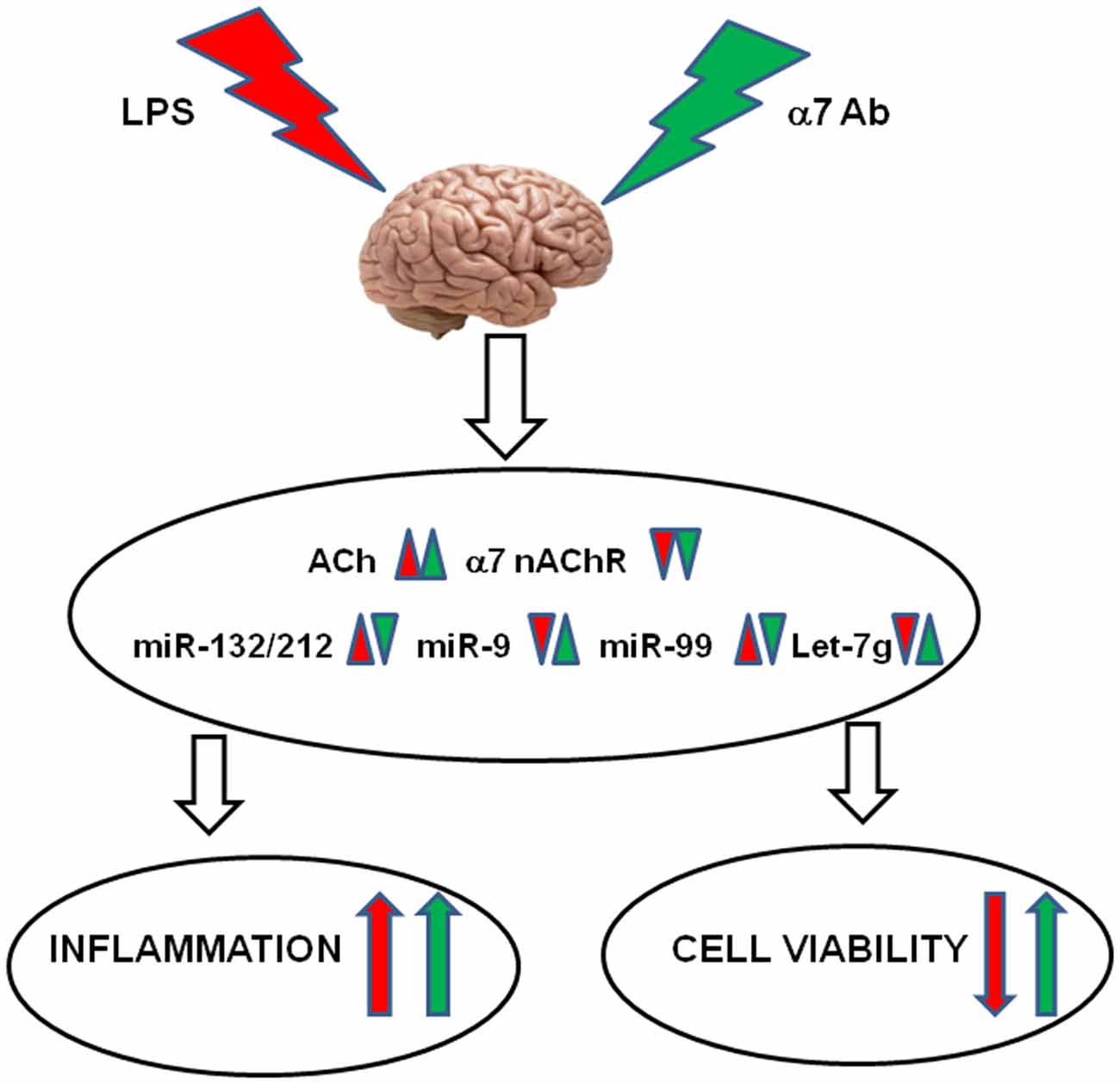
Frontiers | Molecular Mechanisms Regulating LPS-Induced Inflammation in the Brain | Molecular Neuroscience
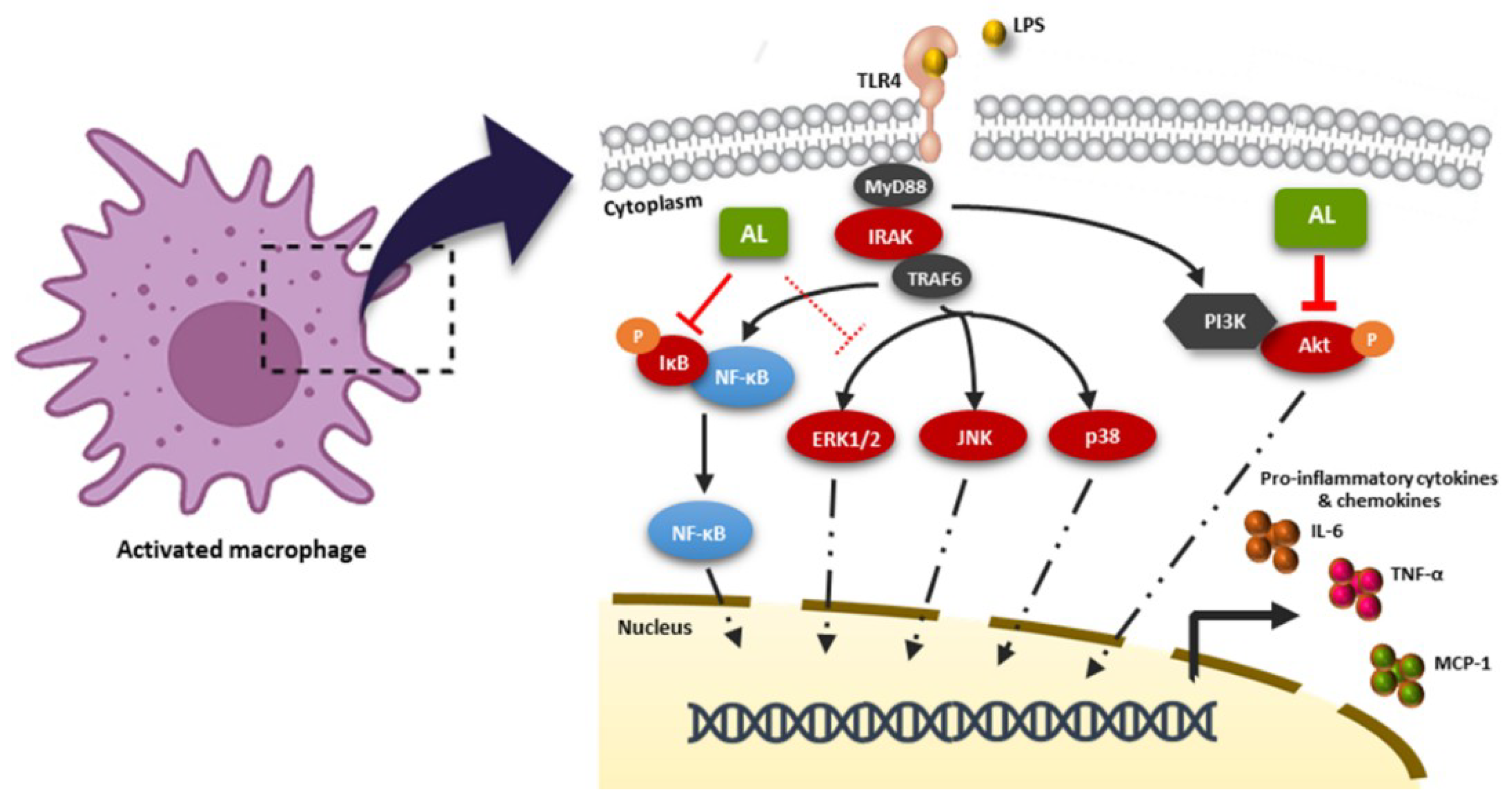
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Artocarpus lakoocha Extract Inhibits LPS-Induced Inflammatory Response in RAW 264.7 Macrophage Cells
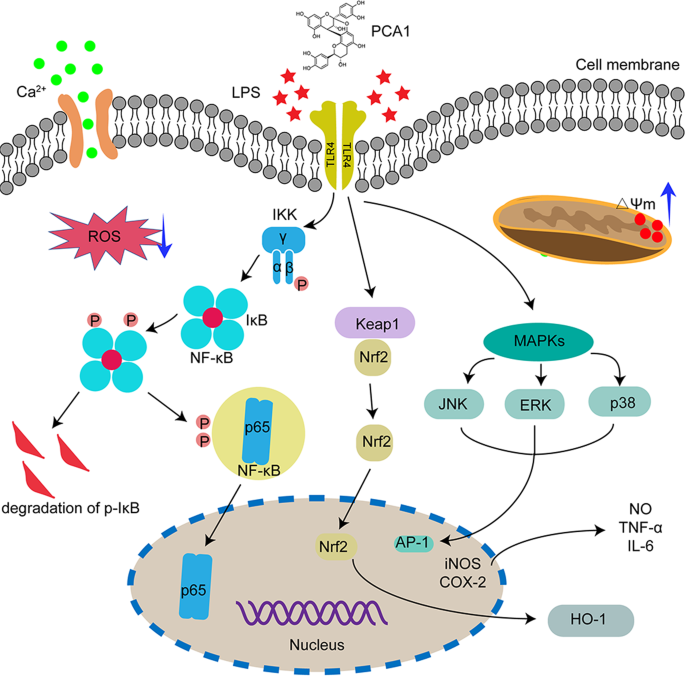
Procyanidin A1 Alleviates Inflammatory Response induced by LPS through NF-κB, MAPK, and Nrf2/HO-1 Pathways in RAW264.7 cells | Scientific Reports
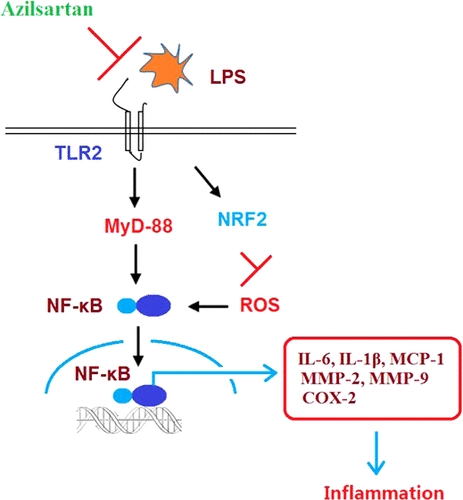
Azilsartan Suppressed LPS-Induced Inflammation in U937 Macrophages through Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Inhibiting the TLR2/MyD88 Signal Pathway. - Researcher | An App For Academics

Cannabidiol prevents LPS‐induced microglial inflammation by inhibiting ROS/NF‐κB‐dependent signaling and glucose consumption - dos‐Santos‐Pereira - 2020 - Glia - Wiley Online Library
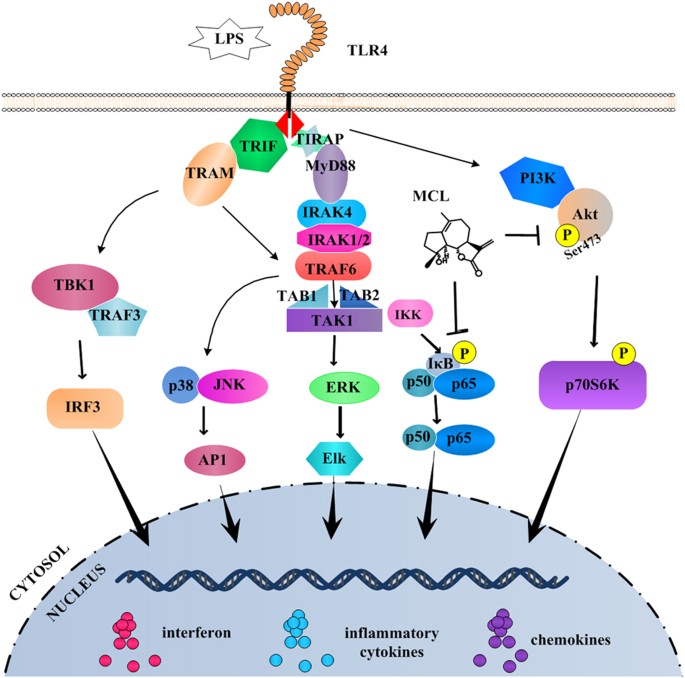
Micheliolide inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory response and protects mice from LPS challenge | Scientific Reports

Amelioration of 4-methylguaiacol on LPS-induced inflammation in THP-1 cells through NF-κB/IκBα/AP-1 and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway - ScienceDirect